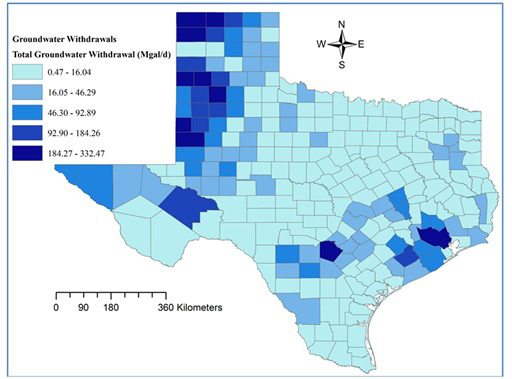
Description
The Gulf Coast aquifer extends from the northeastern Texas-Louisiana Border to the south border of Texas with Mexico. What else does water have to do with the population pressure and change in climate? Evaporation increases as a result of heat increases, part of the greenhouse effect (IPCC). These issues are “local in [its] specifics, yet global in [its] relevance.”
External Resources
- Watertoolbox.us:
http://watertoolbox.us/intro/f?p=689:1
Most recent release of downscaled CMIP5 projections for temperature and precipitation, extends out to 2100 - U.S. Drought Monitor (Texas):
http://droughtmonitor.unl.edu/Home/StateDroughtMonitor.aspx?TX
Useful site to assess drought conditions, and includes links to drought planning resources - Climate Ready Water Utilities Toolbox:
http://www.epa.gov/safewater/watersecurity/climate/toolbox.html
EPA site providing access to climate-related information relevant to the water sector
Reference
- Anderson, F. and Al-Thani, N. (2016) Effect of Sea Level Rise and Groundwater Withdrawal on Seawater Intrusion in the Gulf Coast Aquifer: Implications for Agriculture. Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 4, 116-124. doi: 10.4236/gep.2016.44015. http://file.scirp.org/pdf/GEP_2016042815190220.pdf