Description
Sea level rise is a product of rising ocean temperatures; melting of ice caps, glaciers, and the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets; and anthropogenic disturbances to the water budget (ex. groundwater withdrawal resulting in subsidence of coastal areas). Coastlines are changing dramatically with shoreline erosion, ocean acidification, warming temperatures, coastal subsidence and wetland loss and fluctuations in precipitation patterns. "Relative sea level along the Gulf Coast from Houston-Galveston to Mobile, Alabama, is likely to increase by at least one foot across the region and possibly by as much as six to seven feet in some parts of the Gulf Coast area during this century" (Us Global Change Research Program 2014). Taking climate action will improve the quality of the coastal environment and help mitigate the negative impacts of a changing system.
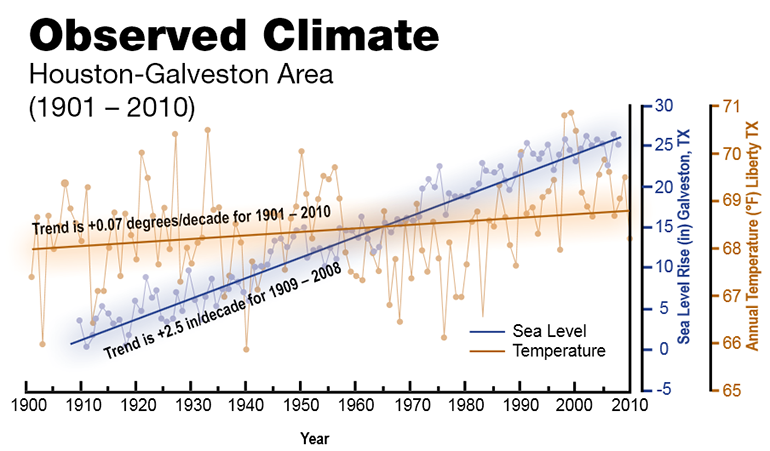 Observed Temperature and Sea Level Rise Increases in the Houston-Galveston Area, 1901-2010.
(Photo Credit: NASA Source)
Observed Temperature and Sea Level Rise Increases in the Houston-Galveston Area, 1901-2010.
(Photo Credit: NASA Source)
 NOAA NCDC - Projected Changes in Soil Moisture for the Western U.S.
(Photo Credit: NASA Source)
NOAA NCDC - Projected Changes in Soil Moisture for the Western U.S.
(Photo Credit: NASA Source)
External Resources
- CDC National Environmental Public Health Tracking Program, Climate Change:
http://tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov/sltrends/sltrends.html
NOAA site for examining measured sea level rise and trends: Averages viewable by season, annual variations, and total change expected in 100 years. - CDC National Environmental Public Health Tracking Program, Climate Change:
http://coast.noaa.gov/digitalcoast
NOAA comprehensive site for coastal data, analysis tools, and training for climate adaptation planning: - Risk Finder Web Tool :
Houston Area ( analysis , and sea level and flood risk projections ) - Sea-Level Change Curve Calculator:
http://www.corpsclimate.us/ccaceslcurves.cfm
Sea-level rise modeling tool: Zoom to your location on the map to see relative change projections, tidal datums and extreme water levels in your area. - Surging Seas Risk Zone Map:
http://ss2.climatecentral.org - US Global Change Research Program. 2014.
Observed Trends and Projected Future Conditions For Climate Change Preparedness and Resilience.
http://www.globalchange.gov/sites/globalchange/files/CCPR_HOU_brochure-final.pdf

